modified carpal compression test|positive test for carpal tunnel : exporters Carpal Compression Test (Apply pressure with thumbs over the median nerve within the carpal tunnel, located just distal to the wrist crease. The test is positive if the patient responds with numbness and tingling within 30 . web4 Replies. Full archive of her photos and videos from ICLOUD LEAKS 2024 Here. Look at Paola Lázaro’s sexy social media photos and screenshots with a semi-naked scene from .
{plog:ftitle_list}
top Introduction Language packs are small files which can be .
Step 1. Patient position in standing or sitting. Step 2. The patient forearm is supinated and then the examiner applies direct pressure over the carpal tunnel (median nerve) between the thenar and hypothenar eminence for 30 seconds. Step 3. A positive test indicates any numbness, .
Purpose [edit | edit source]. Tinel's test is used to test for compression .Modified Reverse Phalen’s Test (AKA Wormser’s Test): Patient places palms together, increasing pressure in the carpal tunnel. Positive result occurs if patient develops paresthesia . Carpal Compression Test (Apply pressure with thumbs over the median nerve within the carpal tunnel, located just distal to the wrist crease. The test is positive if the patient responds with numbness and tingling within 30 .lon-modified Moberg pick-up test (DMPUT) to quantify dexterity at the onset of treatment and compare scores with es-tablished norms. Clinicians should not use the PPB test, Jebsen .
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the most common upper extremity nerve compression syndrome. Patients with CTS experience reduced sensation, dexterity, and function. Irreversible changes in nerve structure and . The manual carpal compression, or Durkan test is performed by applying pressure over the transverse carpal ligament for 30 seconds . Pain or paresthesia indicates a .
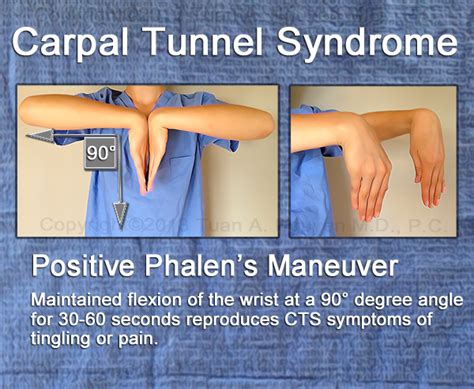
what is a positive phalen test
sign, the carpal compression test, and the wrist ratio index, as well as the CTQ-symptom severity scale and CTQ-functional scale or the Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand .To conduct the test, the patient’s forearm is supinated and the examiner compresses the carpal tunnel between the thenar and hypothenar eminence for 30 seconds. The test is considered positive if symptoms such as paresthesia, . The 'Scratch Collapse Test' (SCT) has emerged as a new provocative test to assist in the localisation of peripheral nerve compression. Clinical prediction rules (CPR), specifically for the Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, .
Sensitivity for the pneumatic compression and the modified pneumatic compression tests were 68% and 84%, respectively. Specificities for these tests were 97% and 95%, respectively. The modified pneumatic compression test demonstrated high sensitivity and specificity for CTS. This test facilitated the diagnosis and was easy to use.DOI: 10.1016/J.JHSE.2007.06.016 Corpus ID: 21284206; The Pneumatic Compression Test and Modified Pneumatic Compression Test in the Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome @article{Tekeolu2007ThePC, title={The Pneumatic Compression Test and Modified Pneumatic Compression Test in the Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome}, author={Ibrahim Tekeoğlu . The pneumatic compression test was performed by wrapping a blood pressure cuff around the wrist and inflating it to 100 mm/Hg for 30 seconds.The modified pneumatic compression test was essentially the same, but with a specially designed wooden pencil-like object of 8 cm length and 8 mm diameter under the cuff in the carpal region and lying along . Fifteen provocative carpal tunnel syndrome tests that fall into the neutral/no decision category include: the carpal compression test, 32 tourniquet test, 32 hand elevation test, 33 Phalen's wrist .
The highly recommended tests were found to be the Phalen's, Tinel's test for carpal tunnel and cubital tunnel, and modified compression test, scaphoid shift test, and elbow flexion test. A total of 14 tests met our requirements to be considered a recommended test.
Objectives: To assess the diagnostic properties of the carpal compression test (CO when performed with the Durkan carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) gauge, and to determine the measurement validity of the gauge. Background: The CCT has been reported to be highly sensitive (37-.89) and specific (.93- 1.0) in the diagnosis of CTS when it is done with .In 1947, when W. Russell Brain described compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel, he concluded that occupation is one of the causal factors. 1; Description. The median nerve compression test is also called Durkan’s test. Mostly commonly, compression of the median nerve results in carpal tunnel syndrome. Pathophysiology The highly recommended provocative tests were found to be the Phalen's, 9 Tinel's, 10 and modified compression test 11 for carpal tunnel syndrome; the scaphoid shift test 12 for scapholunate instability; and the Tinel's 13 and elbow flexion test 13 for cubital tunnel syndrome . Test Author, yearThis study found that the instrumented carpal-compression test had an 89% sensitivity and a 96% specificity in diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome. The instrumented device described in this study is lightweight and simple to use, and provides a rapid and inexpensive method of screening for carpal tunnel syndrome.
Phalen’s test (pushing the dorsal surface of hands together and holding 30 – 60 seconds) Carpal Compression Test (Apply pressure with thumbs over the median nerve within the carpal tunnel, located just distal to the wrist crease. The test is positive if the patient responds with numbness and tingling within 30 seconds.) Introduction. Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is caused by the compression of the median nerve in the carpal canal and is the most prevalent compression neuropathy of the upper extremity (UE). 1 The prevalence of CTS has been estimated to be 6% in men and 9.2% in women. 1 Symptoms include pain, tingling, and numbness in the palmar surface of the radial .
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is caused by compression of the median nerve as it travels through the carpal tunnel. Patients commonly experience pain, paresthesia, and, less often, weakness in the . There is insufficient evidence available to determine the usefulness of the finger flexion wrist flexion with compression test, flick test, Luthy sign, lunate press test, modified carpal compression (that used oscillations over carpal tunnel) test, modified pneumatic compression test, Tanzer test, tethered median nerve tests, current perception .The purpose of this study was to examine the diagnostic value of a new provocative test, the 'modified pneumatic compression test' in . The pneumatic compression test and modified pneumatic compression test in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2007 Dec;32(6):697-9. doi: 10.1016/J.JHSE.2007.06.016. .The modified Duran test had the highest positivity rate, according to the . carpal compression test. CTS can result from ischemia and mechanical compression of the median nerve. In Duran’s .
Durkan Test or as it called the carpal compression test is used to test for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome CTS where the median nerve is compressed in the carpal tunnel of the wrist. It was first described by JA Durkan in 1991. .
modified phalen test, tinel sign, standard carpal compression test (SCCT) and modified carpal compression test (MCCT). Subsequently, electrodiagnostic studies were conducted to confirm the diagnosis of CTS. Sensitivities, specificities, predictive values and likelihood ratio for each and all combinations of a provocative test were determined. Carpal tunnel tests evaluate wrist and finger movement, strength, and sensation. . Both CTS and CuTS are related to nerve compression, but they affect different parts of the wrist and arm. Keep .
The pneumatic compression test and modified pneumatic compression test in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2007; 32:697–699. [Google Scholar] 11. Gillenson SP, Parets N, Bear-Lehman J, Stanton DB. The effect of wrist position on testing light touch sensation using the Semmes–Weinstein pressure aesthesiometer: a . Modified Phalen's test consists of the traditional Phalen's test maneuver of holding the wrists in a position of fixed flexion and the use of a Semmes-Weinstein 2.83-unit monofilament. The filament ( arrow ) is applied perpendicular to the skin surface until it bends.
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the most common upper extremity nerve compression syndrome. Patients with CTS experience reduced sensation, dexterity, and function. Irreversible changes in nerve structure and function due to demyelination and axonal damage can occur in long-standing cases. Published in the May 2019 issue of JOSPT, clinical .
Purpose [edit | edit source]. The Spurling's test (also known as Maximal Cervical Compression Test and Foraminal Compression Test) is used during a musculoskeletal assessment of the cervical spine when looking for cervical nerve root compression causing Cervical Radiculopathy.. Technique [edit | edit source]. There are different ways described in the literature to perform .
the Phalen test was positive in eight (16 per cent), and the Tinel percussion test was positive in ten (20 per cent). Of the five subjects for whom the carpal compression test was positive, four had a positive Phalen test, two had a positive Tinel test (Fig. 4), and all five had normal motor and sensory findings on electrodiagnostic studies. The best of these include the carpal compression test. This is done by applying firm pressure directly over the carpal tunnel for 30 seconds. The test is positive when paresthesias, pain, or other symptoms are reproduced. . KnipschildP.G. Prof. Efficacy of provocative tests for diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. The Lancet. 1990 Feb 17; Vol .The test has since been adapted as the Modified Allen test (MAT). In Allen's original test, both hands were tested simultaneously by the examiner compressing one artery of each hand at the same time. . During the Allen test, digital compression of both ulnar and radial arteries at the level of the proximal wrist crease is applied, which .Durkan’s test, or the carpal tunnel compression test, is used to evaluate for carpal tunnel syndrome. The examiner palpates the carpal tunnel and applies suf.
Purpose: To assess for carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). Test Position: Sitting. Performing the Test: With the patient's arm in supination, the examiner applies pressure with his/her thumbs over the median nerve within the carpal tunnel. This is located just distal to the wrist crease. A positive test occurs when the patient complains numbness and tingling in the median nerve distribution .

test to confirm carpal tunnel
webWe're like you: we want a beer that's smooth and easy to drink, but we want it for $2.50/can including delivery. Confirm you're 19+ and let's send you some beer! Express Brewing .
modified carpal compression test|positive test for carpal tunnel